getcwd系统调用学习笔记
系统调用简介
用户层调用的函数原型: char getcwd(char *buf, unsigned long size);
头文件 <unistd.h>
1. This page documents the getcwd(2) system call, which
2. is not defined in any user-space header files; you should
3. use getcwd(3) defined in <unistd.h> instead in applications.
getcwd()会将当前工作目录的绝对路径复制到参数buffer所指的内存空间中,参数maxlen为buffer的空间大小。
如果当前绝对路径长度大于buf的大小,就会返回-1,错误码为ERANGE。如果buf为null,则getcwd()无效
错误码:
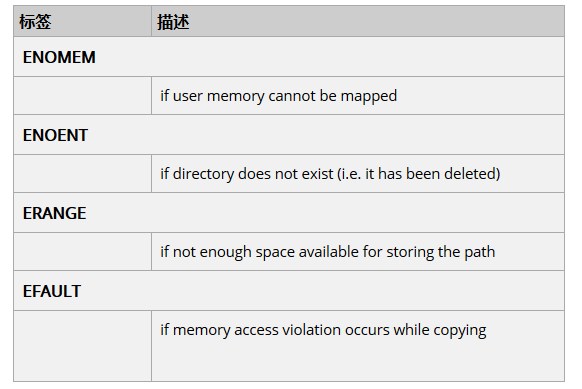
知识点
每个进程都有两个目录相关属性:根目录和当前目录,分别用于解释绝对路径和相对路径
getcwd()会返回当前工作目录的绝对路径,如果当前目录不属于当前进程的根目录(例如:该进程使用chroot设置了一个新的文件系统根目录,但是没有将当前目录的根目录替换成新的)。从linux 2.6.36开始,getcwd会返回“(unreachable)”。通过改变当前目录到另一个挂载的用户空间,普通用户可以完成上述的行为。所以当处理不可信来源的路径时,应该检查返回的路径是否以”/”或”(“开头,避免返回一个不可达地址,被认为是相对地址。
https://github.com/torvalds/linux/commit/8df9d1a4142311c084ffeeacb67cd34d190eff74
getcwd()返回值不应该不含”.”、”..”或符号链接
系统调用源码
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(getcwd, char __user *, buf, unsigned long, size)
{
int error;
struct path pwd, root;
char *page = __getname();
if (!page)
return -ENOMEM;
rcu_read_lock();
get_fs_root_and_pwd_rcu(current->fs, &root, &pwd);
//获取根目录和当前目录项
error = -ENOENT;
if (!d_unlinked(pwd.dentry)) {
unsigned long len;
char *cwd = page + PATH_MAX;
int buflen = PATH_MAX;
prepend(&cwd, &buflen, "\0", 1);
error = prepend_path(&pwd, &root, &cwd, &buflen);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (error < 0)
goto out;
/* Unreachable from current root */
if (error > 0) {
error = prepend_unreachable(&cwd, &buflen);
if (error)
goto out;
}
error = -ERANGE;
len = PATH_MAX + page - cwd;
if (len <= size) {
error = len;
if (copy_to_user(buf, cwd, len))
error = -EFAULT;
}
} else {
rcu_read_unlock();
}
out:
__putname(page);
return error;
}
根据下图可知:get_fs_root_and_pwd_rcu函数就是根据fs结构来获取&root和&pwd
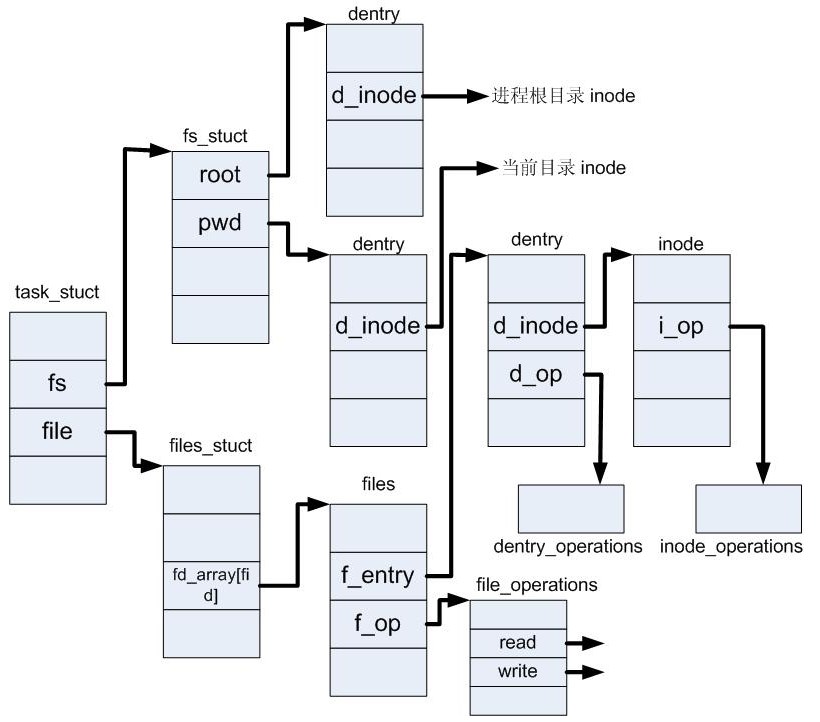
获取当前目录项后,就可以从后往前查找上一级目录,一直找到根目录项,该部分是由prepend_path函数实现:
static int prepend_path(const struct path *path,
const struct path *root,
char **buffer, int *buflen)
{
struct dentry *dentry;
struct vfsmount *vfsmnt;
struct mount *mnt;
int error = 0;
unsigned seq, m_seq = 0;
char *bptr;
int blen;
rcu_read_lock();
restart_mnt:
read_seqbegin_or_lock(&mount_lock, &m_seq);
seq = 0;
rcu_read_lock();
restart:
bptr = *buffer;
blen = *buflen;
error = 0;
dentry = path->dentry;
vfsmnt = path->mnt;
mnt = real_mount(vfsmnt);
read_seqbegin_or_lock(&rename_lock, &seq);
while (dentry != root->dentry || vfsmnt != root->mnt) {
struct dentry * parent;
if (dentry == vfsmnt->mnt_root || IS_ROOT(dentry)) {//判断是否解析到根目录
struct mount *parent = ACCESS_ONCE(mnt->mnt_parent);
/* Escaped? */ //CVE-2015-2925的补丁
if (dentry != vfsmnt->mnt_root) {
bptr = *buffer;
blen = *buflen;
error = 3;
break;
}
/* Global root? */
if (mnt != parent) {
dentry = ACCESS_ONCE(mnt->mnt_mountpoint);
mnt = parent;
vfsmnt = &mnt->mnt;
continue;
}
if (!error)
error = is_mounted(vfsmnt) ? 1 : 2;
break;
}
parent = dentry->d_parent;//保存上一级目录
prefetch(parent);
error = prepend_name(&bptr, &blen, &dentry->d_name);//从后往前读取路径,存在bptr
if (error)
break;
dentry = parent;//从后往前循环处理
}
if (!(seq & 1))
rcu_read_unlock();
if (need_seqretry(&rename_lock, seq)) {
seq = 1;
goto restart;
}
done_seqretry(&rename_lock, seq);
if (!(m_seq & 1))
rcu_read_unlock();
if (need_seqretry(&mount_lock, m_seq)) {
m_seq = 1;
goto restart_mnt;
}
done_seqretry(&mount_lock, m_seq);
if (error >= 0 && bptr == *buffer) {
if (--blen < 0)
error = -ENAMETOOLONG;
else
*--bptr = '/';
}
*buffer = bptr;
*buflen = blen;
return error;
}
prepend_path函数引出CVE-2015-2925:
The prepend_path function in fs/dcache.c in the Linux kernel before 4.2.4 does not properly handle rename actions inside a bind mount, which allows local users to bypass an intended container protection mechanism by renaming a directory, related to a “double-chroot attack.”
参考链接
https://cert.360.cn/warning/detail?id=f28c70a8e4905ec0c912f5cfa02ad198